Introduction. 2
1.
WHY ? (New Regulations) 2
1.1
Basel (Banks and Risk Reporting) 2
1.2
Homeland Security (‘Keep out the Bad Guys’) 2
1.3
Office of Foreign Assets Control (‘Who owns What’) 2
1.4
International Accounting Standards (“Let’s do things Right”) 2
1.5
Patriot Act (‘Keep out the Bad Guys’) 2
1.6
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (‘By the Book’) 3
2.
WHAT ? (BMEWS Data Architecture) 4
2.1
Implications of the Regulations. 4
2.2
Meeting the Regulations. 4
Example
1 : Homeland Security and Patriot Act 5
Example
2 : SOX and CEO of a Public Corporation. 5
Example
3 : Poisoning the Drinking Water 5
2.3
Adding Accountability and Transparency. 6
2.4
Adding Enterprise Data Sources. 6
2.5
The Evolution of Business Intelligence. 7
2.6
The BMEWS Data Architecture. 7
2.7
The BMEWS Data Model 8
4.
HOW ? (General Method à Checklist à Specific Plan) 10
4.1
The BMEWS Method. 10
4.2
Approach. 10
4.3
Legislation and Implications. 11
4.4
Steps in the BMEWS Method. 12
4.5
Analysis of Vendors and Architecture Components. 14
4.6
Analysis of Vendors and Legislation. 15
4.7
Implementation of User Scenarios. 16
4.7.1
: Homeland Security and Patriot Act 17
4.7.2
: SOX and CEO of a Public Corporation. 18
4.7.3
: Poisoning the Drinking Water 19
5 WHO
? (Are You Ready ?) 21
5.1 Readiness Checklist 21
5.2 Getting Started. 21
10.
REFERENCES. 22
This Paper will be
presented at the Enterprise Data Forum in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania on November 5th.
STATUS :-
9.00 am Tuesday,
19th August 2003
Chapter Status
1 OK
2 OK
3 Add more dates for
each ‘Act’
Barry
Williams
August
19th. 2003
Database
Answers Inc.
– My name
is …
The topic I'm going to talk about is
important now and will become increasingly important in the future.
I’d like to leave you with three things :-
1) Something to think about (The Data
Architecture).
2) Something to take away
3) Something to call on in the future,
(Tutorial and Method on Web Site).
I’d like to leave you with three things :-
The Events and results cannot be ignored.
There are a number of Initiatives - Basel
II Accord, Patriot Act, Homeland Security, Sarbanes-Oxley.
1.1 Basel (Banks and Risk Reporting)
– Compliance date – end 2006.
– January 24, 2003
- includes Border, Transportation and Port Security
- The new U.S. Visitor
and Immigrant Status Indication Technology system (U.S. VISIT) entry-exit
system backed by 21st. century technology - is designed to make
entering the U.S. easier for legitimate tourists, students and business
travelers, while making it more difficult to enter the U.S. illegally through
the implementation of biometrically
authenticated documents.
- in its first phase of operation at international air and ports of entry
by end of 2003.
OFAC– (of the Dept. of the Treasury)
OFAC enforces sanctions based on US
foreign policy against targeted foreign countries, terrorists, international
narcotics traffickers, and those engaged in activities related to the
proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
Vendors - Bridger - http://bridgertracker.com/products.htm
- Innovative
systems - http://www.innovativesystems.com/iLytics/secure.htm
- OFAC Compliance - http://www.ofaccompliance.net/
- by 2005.
EU members are mandated to
report financial results as per the IAS by 2005.
– October 26th.
2001
– Became law in October 26th.
2001
- Section 326 – requires identity
verification.
Vendors - Bridger - http://bridgertracker.com/products.htm
The US PATRIOT
Act requires timely and accurate reporting required by industry
regulations.
Impact on IT : Need to create a firm-wide
infrastructure to understand overall position of any client across all business
units
(Extract from :
Fti_data_integration.pdf - Area of IT Spending :
Regulatory reporting)
Financial Enterprise Software
December 2002
© 2002, Financial Technologies
International . Reproduction prohibited. www.ftisoft.com
• Enterprise-wide risk management.
Securities firms are finally coming to understand the
importance of calculating firm-wide risk levels.
Too many firms have been hurt financially by poor risk
management. Firms have too often failed to curb activities of rogue traders
whose activities may sink the entire operation, as was the case
with Barings (the highest-profile case of many) when
one of its traders in Singapore engaged in
illegal trading in Japanese derivatives.
– SOX – enacted July 30th. 2002 in response
to a number of major corporate accounting scandals, eg Enron and Worldcom
- requires company executives to certify the accuracy
and legitimacy of corporate financial statements or face the possibility of
punitive and criminal action.
.
- 23rd.
October 2003 (Governance)
-- 23rd.October 2003 – must
register to do audit work.
-- 15th. June 2004 – additional disclosures required.
Sections 302 and 404(a) deal with the
inernal controls that a company has in place to ensure the accuracy of their
data.
302 – CEOs and CFOs must attest the accuracy
of their company’s quarterly and annual reports:-
1) they have seen the reports.
2) the report contains no false statements,
and leaves nothing material out.
404(a) – originally sept 15th.
2003, then extended to June 15th. 2004
1) Annual report must contain an internal
control report .
aaa
22nd. Augustt - META Group
Poll Shows 90 Percent of Companies Engaged in Sarbanes-Oxley Projects
Sixty-five percent of polled respondents
claim to be actively involved in an ongoing Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) project, while
25 percent are said to be planning to initiate a project in the near term,
according to a META Group, Inc. survey. The results were based on a recent
survey of more than 100 companies regarding their efforts to meet SOX
compliance.
While
SOX is the major lightning rod for compliance initiatives in the U.S.,
along with HIPAA and the USA PATRIOT Act, 88 percent of respondents
from multinational firms claim SOX
projects are managed as global
initiatives.
"Because
of the required high level of preparation on a global scale, many firms will
utilize SOX as a means of improving business efficiency, going beyond what is
merely required to comply," said John Van Decker, META Group's lead
Sarbanes-Oxley compliance analyst and author of the survey. "We expect
company leaders to initiate projects that deploy applications providing
visibility/transparency, financial controls and communications and fraud
protection."
According
to 45 percent of surveyed respondents, CFOs
are the most likely leaders to initiate SOX projects, due to their focus on
financial management. Internal auditors ranked a distant second (24 percent of
respondents). However, an overwhelming majority favor their audit partner for
compliance work (59 percent), and this is contrary to META Group's
recommendation that a third party be used.
"While
this may make the audit attestation process smoother, it limits the multiple
views and guidance that may prove invaluable for a relatively new and untested
regulatory environment," said Van Decker. "Only 6 percent project
that they will use a different audit vendor, and only 3 percent will employ a specialty
compliance vendor." META Group also cautions the 29 percent that believe
they can do this on their own, again pointing to the relatively untested
regulatory environment and the lack of experienced resources (actually none)
internally.
Two implications
(deceptively simple) :-
1) Transparency
2) Accountability
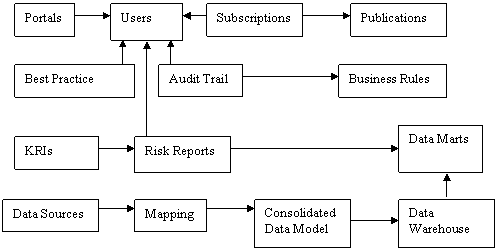
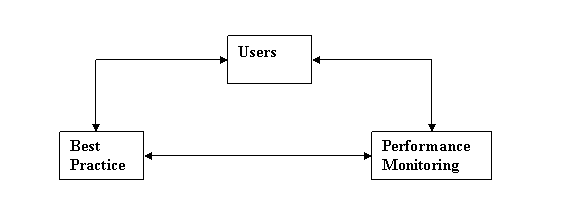
User Scenarios help to provide insight.
This diagram shows the User’s
eye view of the Data Architecture.
If the right things are done
in the right way, then the right (measurable) results should follow.
Therefore, if Users follow
the Best Practice, then their Personal Objectives should be achieved.
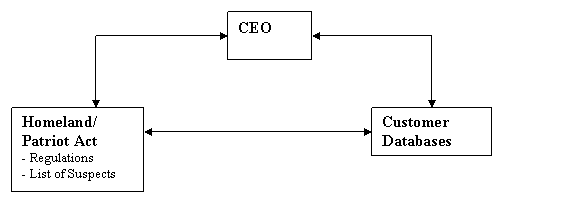
Enterprise Customer
Databases must be matched against Government lists of Suspects.
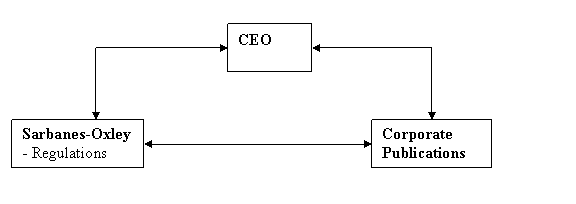
The CEO is legally responsible for the integrity of
the data in all corporate publications – eg annual reports.
Federal or State Regulations require measurement of
chemicals in the Water Supply :-
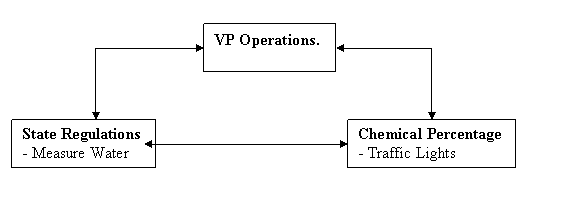
This diagram shows the Data
Architect’s eye view of the Data Architecture –
- adding Accountability and
Transparency.

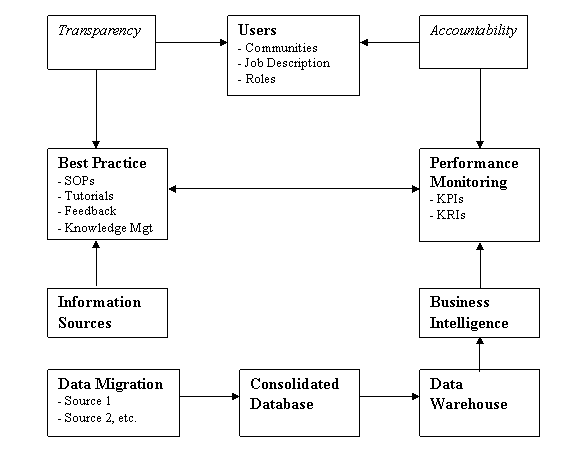
2.4 Adding Enterprise Data Sources
This diagram shows that Enterprise Data Sources
can be integrated using a standard approach.
1) Gartner has coined the term ‘Business Activity
Monitoring’
Companies need to track business processes-such as order
processing, quality
assurance,
inventory, logistics, compliance, etc.- in real time, to improve operational
efficiency as business events are happening. In order to satisfy real-time
business needs.
BI has evolved from Data Warehousing, to
Data Marts, and operational data stores to Performance Monitoring Systems based
on KPIs. These solutions allow business managers to monitor key operational
business events, detect changes or trends and immediately take corrective
action - in real time, or as real-time as appropriate.
If we expand the Users-eye View of the Data
Architecture, we derive this diagram. It shows the major Layers and Components in the Data Architecture to meet
the requirements of the Regulations.
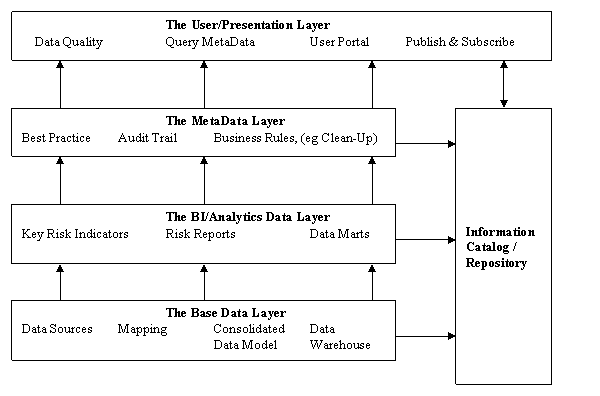
3. WHEN ? (Requirements à Vendors)
Each of the Acts has a timescale.
A number of vendors have produced specific offerings
for the Acts.
Different Enterprises will have different requirements,
depending on the nature of their business.
Different Enterprises will be in different states of
readiness. For example, some may have a Consolidated Customer Data Model.
Others may have Portals and User Performance Objectives in place.
Here are some
timings :-
3.1 Basel II Accord - Banks
must implement by end 2006.
3.2 Homeland Security (US Govt) - First
100 Days - inception on January 24, 2003
3.3 OFAC
3.4 Patriot Act signed into law by President Bush on October 26, 2001.
* penalties up to $1 million, money
laundering, (UK in July)
3.5 Sarbanes-Oxley (CPAs) - 23 Oct 03 - 'initiate
cut-off process'.
Toward the end of July,2003,
Congress passed the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, requiring chief executives and chief
financial officers to certify their company's financial statements as fair,
accurate and consistent with the provisions of the Security and Exchange Act of
1934.
Two provisions in the law that have yet to take effect
may fuel new IT projects.
Section 404, which
public companies must begin to comply with by the end of the year, relates to
the certification of financial reporting and controls.
Section 409, which doesn't
have a clear compliance deadline, calls for companies to report material
financial events as they occur, rather than at the end of their financial
quarter.
Vendor solutions fall into three Categories:-
a) Architecture
Components- eg Data Integration Software
from Ascential or MetaMatrix.
b) Compliance
Software – SOX 1 from Innovative Systems.
c) List of
‘Suspects’ – eg Bridger’s Tracker.
Let’s look at how to produce a Plan …
Therefore what is required is to produce a Plan,
geared to the required End-Point for the Enterprise.
Here are some notes :-
a) Establish which Regulations apply and how.
b) Identify which Vendors offerings apply.
c) Produce a Plan with an acceptable end-date.
The deliverables are tailored Data Dictionary, Data Models,
Templates and Checklist to monitor progress.
This leads to Data-driven
Agile Development,(the subject for another Paper at another time).
These Steps are, of course, Best Practice, and can be
set-up using the BMEWS facilities.
The Method can be applied :-
5.1 Bottom-Up staring with the Base Data
Layer
5.2 Top-Down, starting with the User
Layer,
5.3 Middle-Outwards starting with the
MetaData Layer.
The Information Catalog is populated during the
application of the Method, and can be used to control and track the work so
that progress proceeds to a logical, consistent and complete conclusion.
If you want to do
it, this is how you do it … (and by the way, you don’t have any choice) …
Conceptual --à Specific
Physical --à Integrate with Corporate Data
Architecture.
Therefore, you
need a CDA !!!
1) Assess your
Readiness
2) Gap Analysis
3) Make a Plan to plug the Gaps
3.1 Identify your
Requirements
3.2 Evaluate
Vendor offerings
3.3 Draw up a
detailed Plan.
Patriot Act – signed into Law
by Bush in October 26th. 2001.
Requires that “…all domestic
financial institutions implement [data] screening
policies and establish an independent audit function.
Non-compliance : - Penalties
up to $1,000,000
Screening solutions must
identify suspect Individuals, Organizations and Transactions.
This requires a common
approach to handling Customer information, so that suspect individuals and
organizations within your Database can be easily compared against
government-provided lists.
These lists can be provided
by vendors such as Innovative Systems, and include the OFAC list, the FBI’s
Most Wanted and Fugitive List, and the Bureau of Export Administration’s Denied
Persons List.
Cleansing detail includes :-
Names, aliases, name order, etc..
Therefore we are looking for Customer Data Integration solutions.
i/Lytics
|
|
AREA
|
DATES
|
BEST PRACTICE
|
INDIVIDUAL
(GCDM)
|
ORGANIZATIONS
|
CUSTOMERS
|
TRANS
|
EVENTS
|
ASSETS
|
|
Basel II
|
Banks/Finance
Risk Reports
|
2006
|
Yes
|
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
Homeland
|
Security – Suspects
|
|
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes (Bridger)
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
OFAC
|
Suspects
|
|
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Yes
|
|
Patriot
|
Suspects
|
Oct 2001
|
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
SOX
|
Governance
|
|
Yes
|
|
Yes
|
Yes (Stellent)
|
Yes
|
|
|
Individuals and Organizations
both require matching against Customer Databases.
(TRY TO FIND A FIGURE
OF A MAN WITH A CASE LABELLED ‘bmews’)
BDL. The Base Data
Layer (Bottom-up)
STEP DESCRIPTION DATA
MODELS
These are draft
Steps in the Base Data Layer - Data Sources, ERL and Consolidation.
These include
specification of the Generic Consolidated Data Model.
STEP DESCRIPTION TEMPLATES
BDL.1 Identify the Data Sources.
BDL.2 Identify the Owners of the Data Sources.
BDL.3 Choose a Data Feed and create a Schema using Schema Logic,
(to be confirmed with Carole and Andrei).
3.1 Sample Schema for Hotel Bookings
BDL.4 Choose the Generic Consolidated Data Model,(GCDM).
4.1 DBA Generic Customer
Data Model
4.2 IBM Financial Services Data
Model
4.3 FTI StreetModel
BDL.5 Map the Data Sources to the GCDM.
5.1 Schema Logic
5.2 ToBeDetermined
5.3 ToBeDetermined
6 Choose the Data Warehouse Model.
6.1 DBA Financial Star DW
6.2 DBA Financial Snowflake DW
6.3 DBA Visits Data Warehouse
6.4 IBM Banking Data Warehouse
7 Map the GCDM to the DW.
7.1 Schema Logic
7.2 ToBeDetermined
7.3 ToBeDetermined
8 Choose the Data Marts Model.
8.1 IBM Banking Data
Marts/Templates
8.2 Business Objects
9 Map the DW to the Data Marts.
9.1 Schema Logic
9.2 ToBeDetermined
BI. The BI Layer
(Start in the Middle)
STEP DESCRIPTION DATA
MODELS
BIL.1 Define the Data Marts (in InfoCat)
BIL.2 Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) KPI Derivation.
BIL.3 Define Available Library of Risk Reports Publish
and Subscribe
MDL. The MetaData
Layer (Can Begin Here)
STEP DESCRIPTION DATA
MODELS
MDL.1 Set-up Best Practices Best
Practice Manuals
MDL.2 Define the Business Rules (in InfoCat)
MDL.3 Establish Audit Trail Facilities
MDL.4 Initialize Information Catalog / Data Dictionary Data Dictionary
UL. The User/Content
Layer (Top-Down)
STEP DESCRIPTION DATA
MODELS
UL.1 Set-up Job Descriptions (Content)
UL.2 Set up Publications (eg Library in InfoCat) (Content) FI/KPI Portal Model
UL.3 Create Users Users
and Communities
UL.4 Create Communities
UL.5 Create User Job Responsibilities (Content)
UL.6 Register User Subscriptions Publish
and Subscribe
UL.7 Specify Portal Features Portal
Model
UL.8 Define Data Ownerships and Quality Responsibilities
UL.9 Define User Access Privileges,(eg Query MetaData).
HOW (continued)
Agile Databased Development
4.5 RBW - Add Data Models and Patterns / Templates
Vendors are listed
alphabetically, (MS=Microsoft).
|
LAYER
|
COMPONENT
|
SINGLE
VENDOR
|
BEST-OF-BREED
|
|
User
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Quality
|
|
Ascential, Arhenor, Axio,
Data Quality.
|
|
|
Query MetaData
|
|
Informatica’s SuperGlue.
|
|
|
User Portal
|
IBM (WebSphere Portal)
MS (Shared Portal)
Oracle (Portal Studio)
|
Hummingbird
|
|
|
Publish & Subscribe
|
Oracle AQ.
|
|
|
|
Traffic Lights
|
MS (Digital Dashboard)
|
Ergometrics, Informatica’s
SuperGlue.
|
|
MetaData
|
|
|
|
|
|
Audit Trail
|
|
|
|
|
Best Practice
|
IBM (Content Manager)
|
|
|
|
Business Rules
|
|
eg Clean-up
Scientio - http://www.scientio.com/developers.aspx ,Versata
|
|
Info Catalog
|
|
|
OneData, CA-Platinum, Rochade, Schema Logic, SUN MetaDirectory.
|
|
BI
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Marts
|
IBM (Business Templates) ?
|
Business Objects
|
|
|
KPIs
|
|
Genie Software - http://www.genie-software.com/Products.asp
|
|
|
Risk Reports
|
|
Business Objects
|
|
Base Data
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Sources
|
|
|
|
|
Mapping (ETL)
|
|
Ascential,Informatica,DataJunction,
ETI,MetaIntegration, MetaMatrix.
|
|
|
GCDM
|
IBM,(Fin Services Data
Model).
|
ADRM(?), FTI (StreetModel),
Saphir**
|
|
|
|
|
www.schemalogic.com - Looks good and
offers ASP.
|
|
|
Data Warehouse
|
IBM, (Banking Data Warehouse).
|
SAS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Marts
|
IBM.
|
Business Objects
|
|
|
Reference Data
|
|
Data Foundations (http://www.datafoundations.com)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LEGISLATION
|
VENDORS
|
OTHER WEB SITES
|
|
Basel II Accord
|
|
Bank of International
Settlements,(www.bis.org)
|
|
Homeland
|
Bridger.com
|
|
|
OFAC
|
Compliance
Analyzer - www.ComplianceAnalyzer.com/
|
|
|
|
OFAC Compliance
Software - www.ofaccompliance.com
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Patriot
|
Bridger, Innovative Systems
|
|
|
|
Visual Banker - www.visualbanker.com
|
|
|
SOX
|
Fuego - Automating
financial controls - http://www.fuego.com/
|
Official SOX Reference Site
(www.sarbanes-oxley.com)
|
|
|
Stellent.com Solution helps with Section 404 compliance.
|
|
This Section discusses how some specific Vendor
Products can be used to implement the sample Scenarios.
This diagram shows the User’s
eye view of the Data Architecture.
If the right things are done
in the right way, then the right (measurable) results should follow.
Therefore, if Users follow
the Best Practice, then their Personal Objectives should be achieved.

.

Enterprise Customer Databases must be matched against
Government lists of Suspects
4.7.1.1 The CEO reviews the appropriate Regulations.
4.7.1.2 The CTO the List of Suspects from vendors,(eg Bridger) in compliance with the Homeland and Patriot Acts.
4.7.1.3 The CTO provides background for the list of
corporate Customers.
4.7.1.4 The CTO and CEO reviews the list of Customers
who appear match the List of Suspects.

The CEO is legally responsible for the integrity of
the data in all corporate publications – eg annual reports.
Enterprise Customer
Databases must be matched against Government lists of Suspects
4.7.2.1 The CEO reviews the appropriate Regulations.
4.7.2.2 The CEO specifies the publications that he/she
will review.
4.7.2.3 The CTO provides background for the specified
Publications.
4.7.2.4 The CEO drills down to verify transparency of
the processes involved in the derivation of the data.
4.7.2.5 The CEO drills down to verify the accuracy of
a sample of the transparency of the derived data.
Federal or State Regulations require measurement of
chemicals in the Water Supply :-

The Job
Description for the VP Operations includes responsibility for ensuring that
the drinking water is of an acceptable quality.
Daily measurements must be checked against specific
standards of cleanliness.
This is a bottom-up analysis and monitoring operation.
4.7.3.1 Following his/her Job Description, the Water
Engineer takes a daily sample of the Drinking Water.
4.7.3.2 Values are entered into an online Spreadsheet.
4.7.3.3 The values are summarized and automatically
compared against KPI Threshold values.
4.7.3.4 If Threshold values are exceeded then the
appropriate Traffic Lights change from Green to Red in the Portal Dashboard..
4.7.3.5 The VP Ops notices the Red Traffic Light and
reviews the appropriate Regulations.
4.7.3.6 He/She drills down to the detail and
determines the appropriate action.
4.7.3.7 The Occurrence and the Action are logged and
automatically included in Progress Report.
|
QUESTION
|
IMPORTANCE
|
COMMENT
|
|
USER LAYER
|
|
|
|
-
Job Descriptions include Objectives
|
|
|
|
-
Job Descriptions include Reports and Documents.
|
|
|
|
Does
Information Catalog exist ?
|
|
|
|
Have
Data Owners been identified ?
|
High
|
|
|
BASE DATA LAYER
|
|
|
|
Does
‘Single View Data Model’ available ?
|
Essential
|
|
|
Have
Risk Reporting Requirements been defined ?
|
High
|
|
|
Business
Processes defined ?
|
|
|
|
Etc..
|
|
|
|
STEP
|
USER SIGNOFF
|
TEMPLATE
|
|
Decide
format for Information Catalog
|
|
|
|
USER LAYER
|
|
|
|
-
Check Organization Chart
|
|
|
|
BI LAYER
|
|
|
|
Have
Risk Reporting Requirements been defined ?
|
|
|
|
Business
Processes defined ?
|
|
|
|
Etc..
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BASE DATA LAYER
|
|
|
|
Identify
Data Sources and Owners
|
|
|
|
Rationalize
and Reconcile Data
|
|
|
|
Establish
Data Quality
|
|
|
|
Establish
Data Profiles
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Define
‘Single View Data Model’
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Define
Data Mapping to Single View Model
|
|
|
|
Define
Data Validation Rules
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.1 Adsatis
– Survey of Readiness for Basel Accord
Over half the banks are
adopting Advanced Internal Ratings Based (IRB) Approach
The industry as a whole will
find the Data Management and Data Integration requirements the most onerous.
Is there a ‘Global Reference
Data repository’ ?
10.2 Athenor
Athenor is a Data Cleansing
Suite from Similarity Systems – www.similaritysystems.com
10.3 Basel II Accord
Bank of International
Settlements - www.bis.org.
10.4 Business Rules
– Ilogic – www.ilogic.com – Bracknell - Tel: 01344 661600 - E-mail: [email protected]
– Rules Power - http://www.rulespower.com/
Proof of Concept Methodology
- http://www.rulespower.com/contents/methodology.html
Business Process Modeling.
10.5 Celequest
Business Activity Monitoring -
http://www.celequest.com
Basel Accord :-
Risk
management is a critical aspect of any financial institution’s
operations. Continual monitoring of risk exposure is important not just for
sound fiscal planning, but for early warning signs of potential defaults that
could put an institution at risk.
Celequest’s unique ability to integrate and analyze information from multiple sources in real time
is a vital asset for firms focused on minimizing their risk exposure. For
example, Celequest can be used to monitor loan covenants, combining and
analyzing information on customers’
profitability, inventory levels, sales
etc., and notifying appropriate personnel whenever any of those covenants
are breached.
Celequest can also be used to monitor a firm’s risk
portfolio, alerting managers when the portfolio’s risk level has crossed a
predefined threshold. And, with Celequest these thresholds can be defined as
anything from a simple discrete number to an ‘intelligent threshold’ that indicates the risk level is, for
example, more than 2 standard deviations away from the threshold for more than
4 hours.
Patriot Act Compliance
Compliance with the USA Patriot Act
can be challenging for financial services firms. To do it right, firms must
constantly monitor financial transactions to ensure that they’re not being used
for the benefit of illegal activities. Celequest can help with this difficult
task. Celequest can integrate multiple
sources of internal and external data and dynamically model scenarios where transaction patterns may indicate
possible illegal activity. Once identified, activity can be brought to the
attention of the authorities through automatic
alerts that can be configured within Celequest.
From the Product PDF file …
“Alerts incorporating escalation … go to key business
managers when an exception condition occurs.
“dashboard of alerts can be embedded in a personalized
Portal.”
“Events à Business
Views (Data Models that provide a real-time picture of a business activity.
Rules update the Metrics
Each Business Activity is a collection of possible
Scenarios that identify exceptional business conditions. The Scenario Modeler
defines business activities and defines the Scenarios that monitor the Activities.
“Activity Dashboard has Alerts and KPIs, Workflows and
Drill-downs.
.
Celequest Patriot Act
Compliance with the USA
Patriot Act can be challenging for financial services firms.
To do it right, firms must
constantly monitor financial transactions to ensure that they’re not being used
for the benefit of illegal activities.
Celequest can help with this
difficult task. Celequest can integrate
multiple sources of internal and external data and dynamically model
scenarios where transaction patterns may indicate possible illegal activity. Once
identified, activity can be brought to the attention of the authorities through
automatic alerts that can be
configured within Celequest.
10.6 Data Foundations
One Data :- http://www.datafoundations.com/products/index.htm
10.7 Dublin Core
MetaData Conference
- http://dc2003.ischool.washington.edu/registration.html
- Sept. 28th – Oct.2nd.
10.8 GCDM
Schema Logic
– www.schemalogic.com
Looks good and offers ASP.
"Death of
the Accidental Enterprise –
Architecture
Becoming a Real-Time Enterprise demands the death of the accidental enterprise
architecture and will force companies to focus on application integration in a
strategic way. ”
Gartner Group, 2002
"SchemaLogic
is inhabiting an exciting market space. Your message is powerful, especially
when your customers are large enterprises with strong leadership. The ROI
is rapid. When enterprises have the EAI and messaging tools to transform any
source formatted data to any target format as they do today, it is mandatory
that an authoritative repository of schemas be available for standards
enforcement. I am confident that the SchemaLogic’s technology does do this
well.”
John Hanson, BAAN
10.9 Genie Software
- 01227 451400 http://www.genie-software.com/Products.asp
Business Genie 'Health
Master' has been designed to provide you with a diagnostic check on various key indicators bench-marked to industry standards and past performance.
It is a single use product,
completed on screen. The details submitted require professional attention and
the report is e-mailed back to you after being checked.
10.10 Homeland
Bridger.com
10.11 Informatica
SuperGlue for Visibility ($150K) – drill-down
metadata, dashboard, personalized
directory and portal, role-based.
Informatica's extraction
technology plus presentation layer has applications in new regulatory
environment
Business analytics specialist Informatica has released
what it calls SuperGlue, which will offer metadata (data about data) viewing
capabilities, via a dashboard, to
customers.
Thus, SuperGlue is both underlying technology --
mainly extraction, a Informatica specialty
-- and a presentation layer. 
Metadata has genuine business importance these days
because All CFOs are signing on the dotted line in response to Sarbanes-Oxley,
and when they see a big number, they
want to know the background of where it came from.
Accordingly, SuperGlue can be used as part of the
supporting documents involved in this process, giving the CFO visibility into
the databases from which figures
were culled, what business processes
went into the calculation, and "a look at all the information about that
data”.
For those who really want to dig into their metadata,
SuperGlue offers advanced 'lineage' features that trace the dependencies
between databases. This will be important for enterprises with many data
sources, which is the majority.
“INFORMATICA SUPERGLUE EMPOWERS CIOS WITH GREATER
VISIBILITY AND CONTROL OF ENTERPRISE INFORMATION
Revolutionary new metadata
management software provides audit trail for data, systems and processes across
the enterprise”
Personalized directory-SuperGlue
includes a searchable catalog of an enterprise's information assets, coupled
with their business and technical attributes. This secure knowledge base can be
personalized
by role and can
present logical, physical and process-based
views of assets across all enterprise systems and projects.
10.12 Innovative Systems
– offers software
utilities for Compliance - http://www.innovativesystems.com/
10.13 Knowledge Management
An excellent site – especially
the New - http://www.kmworld.com/news/
What is KM and what kind of
s’w solutions are appropriate ?
Maybe – combination of Best
Practice, Q & A, Feedback, State-of-the-Art, SOPs, Tutorials.
Try ASP trial - http://www.knowledgebase.net/ - Your
order number is 92541 (miami3)
Here’s
a good site :- http://www.kmworld.com/
Best Practice on KM :- http://www.kmworld.com/publications/whitepapers/index.cfm
Provides Hosted Edition,
Professional Edition, Enterprise Edition.
Possible applications :-
KnowledgeBase.net
is the essential application for any business to create, maintain, and share
company knowledge. Popular client applications of KnowledgeBase.net include:
a)
Self-Service
Customer Support
b)
FAQ
Management
c)
Contact Center Knowledge Management
d)
Help
Desk Knowledge Base
e)
Document
Management
f)
Product
/ Project Documentation
10.14 MetaMatrix
MetaMatrixis an
Enterprise-level Data Integration Product – www.metamatrix.com
10.15 MKS
MKS Integrity Manager is a
Workflow Mgt solution to the SOX requirements.– www.mks.com
(with a Graphic Modeller).
10.16 OFAC
10.17 Oracle
Corporate
Governance - http://www.oracle.com/solutions/corporate_governance/
Corporate
Governance is a global concern, but not all geographies are facing the same
challenges. In the United States, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act
introduced strict requirements for a new level of corporate accountability that
fundamentally changes the way US-based businesses report financial information.
In Europe, the mandated adoption of the International Accounting Standards (IAS) by
2005 will ultimately require businesses to review and standardize their
existing processes, practices, and systems to meet the new standard. Oracle can help you respond to the myriad
regulatory demands of the global economy.
Oracle E-Business Suite 11i
has a unified Data Model and BI.
Need improved internal
controls to :-
- Enforce
policies and procedures
- Detect and manage exceptions early.
The weak economy heightens
scrutiny of corporate leadership.
A McKinsey survey identified
that 44% of directors don’t fully understand the key drivers of value for the
organizations they control. (McKinsey – April – May 2002 US Directors Survey)
10.18 Patriot Act
Bridger, Innovative Systems
Visual Banker - www.visualbanker.com
10.19 Reference Database
Kalido – www.kalido.com
10.20 Rules
Scientio – Business Rules
Processor - http://www.scientio.com/developers.aspx
10.21 Sarbanes-Oxley
SOX – www.sarbanes-oxley.com
SOX/PWC -http://www.pwcglobal.com/Extweb/NewCoAtWork.nsf/docid/D0D7F79003C6D64485256CF30074D66C
Fuego - Automating financial
controls - http://www.fuego.com/
‘Sarbanes-Oxley Solution’ -
SOX – from Stellent - www.stellent.com
Based on its Universal
Content Management architecture, which has been deployed by customers for a
variety of compliance processes such as those related to HIPAA, ISO 9000 and
FDA approval, the Sarbanes-Oxley Solution from Stellent
is designed to help companies efficiently manage and approve content related to
financial and non-financial disclosures as well as Section 404 compliance.
Stellent further says the
solution enables companies to address the initial documentation and identification of key processes and
controls as required by the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and automates testing
processes to ease the ongoing resource requirements.
The company adds that the
offering allows all of the various
parties involved in the compliance
process to quickly, easily and securely create, manage, share, track, approve
and archive all information pertaining to disclosures and financial reporting with
minimal training, using only a browser.
The software is personalized
for non-technical business users, such as auditors, accountants and chief
financial officers, and includes an interface that uses field-specific
terminology and guides people through the system.
Stellent says the offering
supports any file type, including rich media files such as earnings conference
calls or videoconferences, and automatically converts content to Web-based
formats, such as HTML or PDF.
Also, Stellent will collaborate
with Protiviti, an internal audit and
business and technology risk consulting firm, to support customers in managing
their Sarbanes-Oxley requirements.
10.22 - Vendor – Visual
Banker
About OFAC
The Office of Foreign Assets
Control (OFAC) of the U.S. Department of the Treasury administers and enforces
a series of new laws that impose economic and trade sanctions against targeted
foreign countries and their agents, terrorism sponsoring organizations and
agencies, and international narcotics traffickers based on U.S. foreign policy and national security goals.
Under these laws, financial
institutes, securities firms, and insurance companies are obligated to block or "freeze" property and payment of
any funds transfers or transactions, and to report all blockings to OFAC within 10 days of occurrence.
Any institution in
non-compliance is open to adverse publicity, fines, and even criminal
penalties.
OFAC acts under presidential
wartime and national emergency powers, as well as authority granted by specific
legislation, to impose controls on transactions and freeze foreign assets under
U.S. jurisdiction.
New Treasury Rules
Recently, as an extension of
the U.S.A. Patriot Act, OFAC created new Rules impacting on financial
institutions. The objective of these Rules is to eliminate "money laundering".
These Rules require all U.S. financial institutions (banks, insurance companies,
credit unions, etc.) to screen new
customers against federal lists of known and suspected terrorists, with an
emphasis on Specially Designated Nationals (SDN).
Executive Responsibility
Responsibility for this
process will be held at the executive level, and must be a component of an
executive involved and approved plan.
U.S.A. Patriot
Act, Section 326
Specifically, Section 326 of
the U.S.A. Patriot Act calls for the
following:
Verify the identity of any
person seeking to open an account.
Maintain records of the
information used to verify the person's identity, including name, address, and
other identifying information,
Determine whether the person
appears on any lists of known or suspected terrorists or terrorist
organizations provided to the financial institution by any government agency.
This means —
Financial institutions must
have a customer identification and
verification program.
All new accounts need to be
screened against OFAC Specially Designated Nationals and other published lists
of blocked persons, criminal suspects, known and suspected terrorists, and
designated terrorist organizations.
Documents used to identify
the new account holder (such as driver's license, passport, social security
card, or credit cards) need to be verified to a reasonable and practical extent
to determine that the identity is valid.
A certified database of all accounts needs to be maintained
containing the name, date of opening, identification presented, and the
identity verifications, with records retained for 5 years after the account is
closed.
Additional related rules are
also coming into effect for other large money-handling interests, such as
lottery corporations and casinos.