Appendix C. Data Quality Checks
Appendix D. Library of Templates
Barry
Williams
1. Introduction
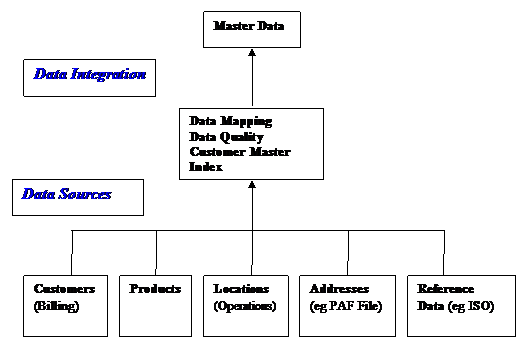
Master Data
Management (‘MDM’) is characterised by the establishment of a single view of
everything which is of importance in an organisation or an area of interest.
This would typically include Customers,
Products and Suppliers.
This Tutorial
covers the basic principles of MDM, including Data Integration and Data
Quality.
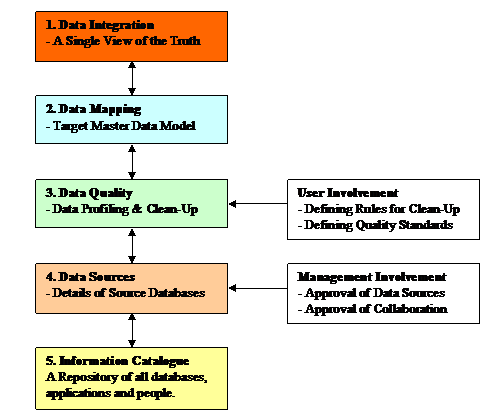
2. User Involvement
User involvement
is am essential part of every successful MDM activity.
At the senior
levels, management will need to approve collaboration on the part of Data Owners and Stewards.
If Data Governance
is in place, this will require compliance with the appropriate procedures.
If Governance is
not in place, then these MDM activities will be the first steps in that
direction.
This is shown by
the two plain white boxes on the right-hand side of the next Diagram.
3. Stages in MDM
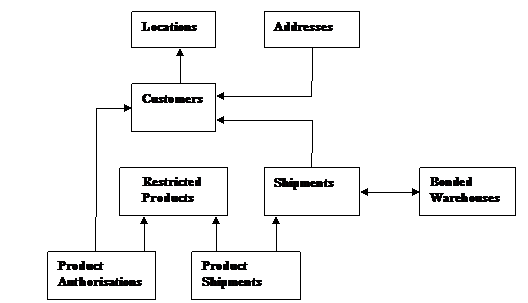
4. MDM Data
Model
This diagram shows relationships between the logical ‘Things of Interest’ in the MDM Data Model.
This is a Logical diagram which is slightly different
from the Physical diagram, which would be based on Database Tables.
5. The MDM Process
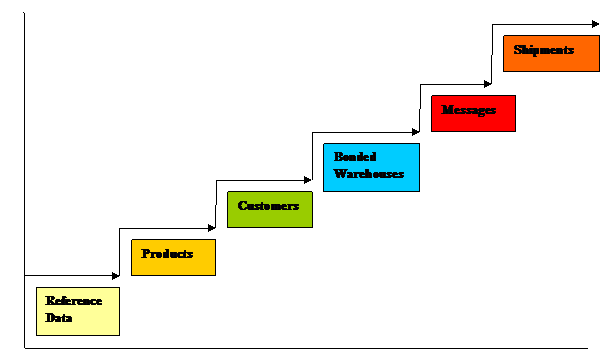
6. The Data Platform
Arrows in the diagram show that
data has to be loaded into a Database in a sequence that reflects the logical
dependence between different sets of data.
The major sets of Data include
Reference Data, Products, Customers, Warehouses, Messages and Shipments.
7. User Scenarios
This
Scenario shows the Steps and the implications for Master Data.
It can
be used to identify, on a CRUD basis, where Master Data is used
In
other words, it validates that the MDM is adequate and will support the User Scenarios.
|
Nr |
DESCRIPTION |
MDM IMPLICATIONS |
|
1 |
Register as a Customer |
- Single View of
each Customer - Standard Location
List |
|
2 |
Request Product
Authorisation |
- Single View of
each Product |
|
3 |
Requests
permission for a Shipment |
- Single View of
each Product |
|
|
|
|
8. Tutorial Summary Steps
This
Scenario shows the Steps and the implications for Master Data.
8.1
Establish Reference Data.
8.2
Identify Data Sources, with Data Models and Data Items for each Source
8.3
Create Target Data Model, as shown in Section 3.
8.4
Define Data Mapping Specifications from Sources to Targets.
8.5
Asses Data Quality and improve as necessary
8.6
Determine sources of required Data
8.7
Create Scripts to load required Data
8.8
Create Scripts to verify required Data loaded OK
9. Tutorial Detailed Steps
This
Scenario shows the Steps and the implications for Master Data.
9.1 Establish Reference Data, for example
:-
- Country Codes
- Language Codes
- Product Categories
This
uses the RefData.1 Template.
|
DATA |
SOURCE |
COMMENTS |
|
Country
Codes |
ISO |
|
|
Language
Codes |
ISO |
|
|
Product
Categories |
Oracle
Database |
|
|
Customers
Operator Type |
Oracle
Database |
|
9.2 Identify Data Sources, with Data
Models and Data Items
This
uses the GlossDataSrc.1 Template.
|
DATA |
SOURCE |
COMMENTS |
|
Location |
Operations |
|
|
Products |
SIC Products
|
|
|
Customers |
Billing |
|
9.3 Create the Target Data Model
- This requires identifying Logical
Entities which have to be validated against physical Tables.
9.4 Determine the sources of the required Master
Data
- Reference Data
- Products
- Customers
- Etc.
9.5 Asses Data Quality and improve as
necessary
- This requires defining Rules for Data
Validation and Clean-Up.
This
uses the Rules.1 Template.
|
RULE |
CONDITION |
DETAILS |
|
TR.1 |
Check
that Names are unique |
Ensure
that & is not used as AND in a Customer
Name |
|
TR.2 |
Check
that Names are unique |
Ensure
that LTD is not used as LIMITED in a Customer
Name, ir vice versa. |
9.6 Define Data Mapping Specifications
from Sources to Targets.
- This requires defining Rules for Data
Transformation
This
uses the MapSpecs.1 Template.
|
SOURCE |
TARGET |
|||||
|
Table |
Field |
Data
Type |
Transformation
Rules |
Table |
Field |
Data
Type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.7 Create Scripts to load required Data
- This can be done bespoke, using SQL Templates or a product such as
Business Objects Data Integrator.
9.8 Create Scripts to verify required Data
loaded OK
- These Scripts control the overall Data
Loading process and can be implemented using different techniques,
depending on the technical environment.
Appendix A. Glossary of Terms
The purpose of
this Glossary is to establish a shared understanding of the Terms in common
use.
|
TERM |
SOURCE |
DEFINITION |
DESCRIPTION |
|
CBS |
Data
Architecture document in the Repository. |
Corporate Billing System |
The CBS is major
repository for all the details of every Customer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Appendix B. Reference Data
B.1 ISO Country Codes
Here are ten important Country Codes :-
SELECT
code,description
FROM iso_country_codes
WHERE code IN
('AE','AF','AU','CN','EG','FJ','GB','MN','MY','US')
ORDER BY description
|
CODE |
DESCRIPTION |
|
AF |
|
|
AU |
|
|
CN |
|
|
EG |
|
|
FJ |
|
|
MY |
|
|
MN |
|
|
AE |
|
|
GB |
|
|
US |
|
B.2 ISO Language Codes
These values have
been established by the International Standards Organisation (ISO).
This shows 23
typical values.
SELECT
code,description
FROM iso_language_codes
ORDER BY description
/
|
CODE |
DESCRIPTION |
|
bg |
Bulgarian |
|
cs |
Czech |
|
da |
Danish |
|
nl |
Dutch |
|
en |
English |
|
et |
Estonian |
|
fi |
Finnish |
|
fr |
French |
|
de |
German |
|
el |
Greek |
|
gr |
Greek (Latin
character) |
|
hu |
Hungarian |
|
it |
Italian |
|
lv |
Latvian, Lettish |
|
lt |
Lithuanian |
|
mt |
Maltese |
|
pl |
Polish |
|
pt |
Portuguese |
|
ro |
Romanian |
|
sk |
Slovak |
|
sl |
Slovenian |
|
es |
Spanish |
|
sv |
Swedisch |
Appendix C. Data Quality Checks
C.1
Customer Address Validation
This check
identifies situations where the same Customer has different Addresses.
Here’s the SQL :-
SELECT
DISTINCT CUSTOMER_NAME,CUSTOMER_ID,ADDRESS_LINE1
FROM BILLING_CUSTOMERS
WHERE
CUSTOMER_NAME LIKE 'JOE BLOGGS%'
ORDER
BY CUSTOMER_NAME
And here are some fictitious Results :-
|
CUSTOMER_NAME |
CUSTOMER_ID |
ADDRESS LINE 1 |
|
JOE
BLOGGS LTD |
12345678 |
UNIT 1 |
|
JOE
BLOGGS LTD |
12345678 |
UNIT 1 INDUSTRIAL
ESTATE |
C.2 Customer Names Duplication
This check looks
for multiple Records to identify the fields that define uniqueness.
Here is the SQL
that shows multiple records for Customer Name, BILLING_ORGN_ID, VAT Number and
Suffix :-
SELECT
CUSTOMER_NAME,CUSTOMER_ID,COUNT(*)
FROM Customers
GROUP BY CUSTOMER_NAME,CUSTOMER_ID
HAVING
COUNT(*)>1
ORDER BY CUSTOMER_NAME,CUSTOMER_ID
/
and here are some fictitious results :-
These Names that
have been anonymised so that actual Customers cannot be identified :-
|
CUSTOMER_NAME |
CUSTOMER_ID |
COUNT |
|
JOE
BLOGGS LTD |
12345678 |
4 |
|
JOE
BLOGGS LTD |
12345678 |
4 |
C.3 Customer Names Validation
Check 1. Checking for the same Customers having different
Names.
Here’s the SQL :-
SELECT DISTINCT CUSTOMER1.CUSTOMER_NAME
AS CUSTOMER1
, CUSTOMER2.CUSTOMER_NAME
AS CUSTOMER2
FROM BILLING_CUSTOMERS CUSTOMER1
,BILLING_CUSTOMERS CUSTOMER2
WHERE CUSTOMER1.CUSTOMER_ID
= CUSTOMER2.CUSTOMER_ID
AND CUSTOMER1.CUSTOMER_NAME != CUSTOMER2.CUSTOMER_NAME
ORDER BY CUSTOMER1.CUSTOMER_NAME
Here are some fictitious results.
These Names that
have been anonymised so that actual Customers cannot be identified :-
|
CUSTOMER NAME |
|
ABLE & CAIN |
|
ABLE AND CAIN |
|
JOE BLOGGS LTD |
|
JOE BLOGGS
LIMITED |
|
SMITH &
WESSON |
|
SMITH AND WESSON |
Appendix D. Library of Templates
This Appendix
defines which Templates are used in MDM.
Many of these
Templates are also used in other areas of Data Analysis.
They are collected
here for convenience.
D.1
Data Validation Rules
This applies to a
number of conditions, such as Customer Name Validation
Template Number : Rules.1
|
RULE |
CONDITION |
DETAILS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D.2
Glossary of Data Sources
This applies to a
number of Sources for important types of Data, such as Locations, Products and Customers.
Template Number : GlossDataSrc.1
|
DATA ITEM |
SOURCE |
COMMENTS |
|
Location |
OPERATIONS |
|
|
Products |
Restricted
Products Table |
|
|
Customers |
BILLING |
|
D.3
Mapping Specifications
This applies
wherever data is migrated from any Source to any Target.
Template Number : MapSpecs.1
|
SOURCE |
TARGET |
|||||
|
Table |
Field |
Data
Type |
Transformation
Rules |
Table |
Field |
Data
Type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D.4
Reference Data
The purpose of
this Template is simply to place on record the Reference Data and appropriate
details.
Template Number : RefData.1
|
DATA |
SOURCE |
COMMENTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|